Hello!
We have our last exam on Friday. It is a review of the previous exams.
We have our last exam on Friday. It is a review of the previous exams.
-1st: NUMBERS (1-9,999); ORDINAL AND CARDINAL
-2nd: VOCABULARY
REMEMBER: In each sentence, only can be one yellow card.
How to form the Past Tense in English
The main rule is that for every verb in English, there is only one form of it in the past tense.
(The exception is the Past tense of To Be, which has two forms: was and were)
(The exception is the Past tense of To Be, which has two forms: was and were)
For example: The past tense of the verb want is wanted.
Wanted is used as the past tense for all subjects/pronouns.
- I wanted
- You wanted
- He wanted
- She wanted
- It wanted
- We wanted
- They wanted
Past Tense Regular Verbs
To change a regular verb into its past tense form, we normally add –ED to the end of the verb.
- play – played
- cook – cooked
- rain – rained
- wait – waited
Examples of sentences using regular verbs in the past tense
- Last night I played my guitar loudly and the neighbors complained.
- She kissed me on the cheek.
- It rained yesterday.
- Angela watched TV all night.
- John wanted to go to the museum.
Negative sentences in the Past Tense
We use didn't (did not) to make a negative sentence in the past tense.
This is for regular AND irregular verbs in English.
(Exception is To Be and Modal Verbs such as Can)
This is for regular AND irregular verbs in English.
(Exception is To Be and Modal Verbs such as Can)
Compare the following:
Present: They don't live in Canada.
Past: They didn't live in Canada.
Past: They didn't live in Canada.
The main verb (live in the example above) is in its base form (of the infinitive). The auxiliary DIDN'T shows that the sentence is negative AND in the past tense.
NOTICE: The only difference between a negative sentence in the present tense and a negative sentence in the past tense is the change in the auxiliary verb.
Both don't and doesn't in the present tense become didn't in the past tense.
Compare the negative sentences in the examples below:
Present: You don't need a mechanic.
Past: You didn't need a mechanic.
Past: You didn't need a mechanic.
Present: You don't walk to work.
Past: You didn't walk to work.
Past: You didn't walk to work.
Present: He doesn't speak Japanese.
Past: He didn't speak Japanese.
Past: He didn't speak Japanese.
Examples of negative sentences in the Past Tense
- I didn't want to go to the dentist.
- She didn't have time.
- You didn't close the door.
- He didn't come to my party.
- They didn't study so they didn't pass the test.
- We didn't sleep well last night.
Questions in the Past Tense
We use did to make a question in the past tense.
This is for regular AND irregular verbs in English.
(Exception is To Be and Modal Verbs such as Can)
This is for regular AND irregular verbs in English.
(Exception is To Be and Modal Verbs such as Can)
Compare the following:
Present: Do they live in France?
Past: Did they live in France?
Past: Did they live in France?
The main verb (live in the example above) is in its base form (of the infinitive). The auxiliary DID shows that the question is in the past tense.
NOTICE: The only difference between a question in the present tense and a question in the past tense is the change in the auxiliary verb.
Both Do and Does in present tense questions become Didn't in past tense questions.
Both Do and Does in present tense questions become Didn't in past tense questions.
Compare the questions in the examples below:
Present: Do you need a doctor?
Past: Did you need a doctor?
Past: Did you need a doctor?
Present: Do you ride your bike to work?
Past: Did you ride your bike to work?
Past: Did you ride your bike to work?
Present: Does he live in Italy?
Past: Did he live in Italy?
Past: Did he live in Italy?
We can also use a question word (Who, What, Why etc.) before DID to ask for more information.
- Did you study? – Yes, I did.
- When did you study? – I studied last night.
- Where did you study? – I studied at the library.
Read more about short answers in the past tense.
Examples of Questions in the Past Tense
- Did you go to work yesterday?
- Did they arrive on time?
- Did she like the surprise?
- Where did she go?
- What did you do yesterday?
- What did you say? - I didn't say anything.
- Why did we have to come?
Irregular Verbs in the Past Tense
Irregular verbs are ONLY irregular in affirmative/positive sentences.
(An exception to this is with the verb TO BE in the Past Tense).
(An exception to this is with the verb TO BE in the Past Tense).
For example: The past tense of GO is WENT.
It does not end in –ED so it is considered irregular.
It does not end in –ED so it is considered irregular.
The word went is used for all subjects – I, you, we, they, he, she, it.
- I went to the beach
- He went to the park.
- She went to the zoo.
- They went to the library.
BUT, as we mentioned before, it is only in its irregular form (went) in sentences that are affirmative/positive.
Compare the following using GO in the past tense.
- They went to the beach
- They didn't go to the beach --- Didn't shows that we are talking in the past tense.
- Did they go to the beach? --- Did shows that we are talking in the past tense.
Another example with an irregular verb.
The past of EAT is ATE.
The past of EAT is ATE.
- You ate my cake.
- You didn't eat my cake.
- Did you eat my cake?
Present vs Past Tense Summary Chart
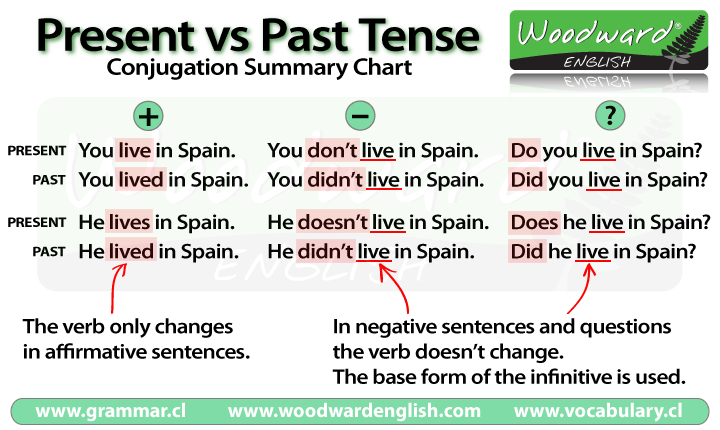
- IRREGULAR VERBS:
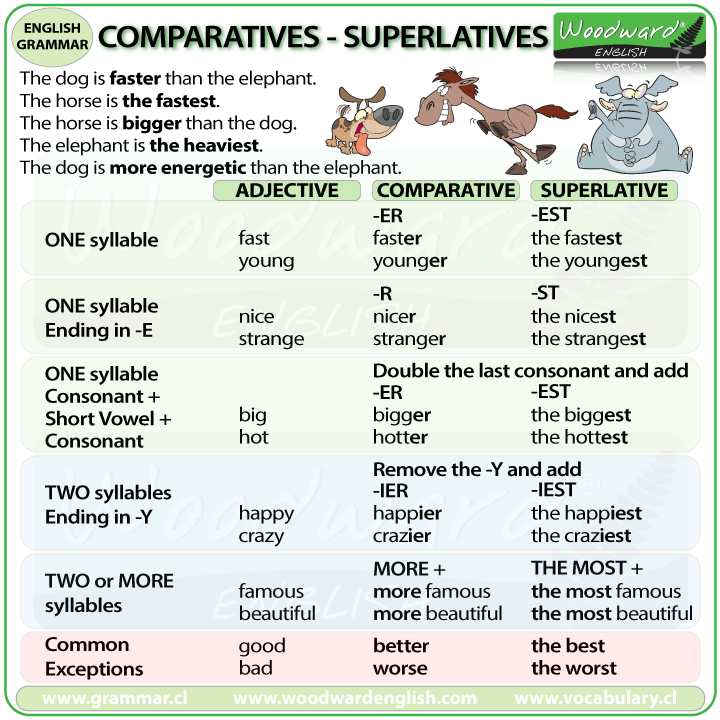
-4th: ADJECTIVES
You only have to study the ones that are highlighted in your page.
-5th: Wh-QUESTIONS
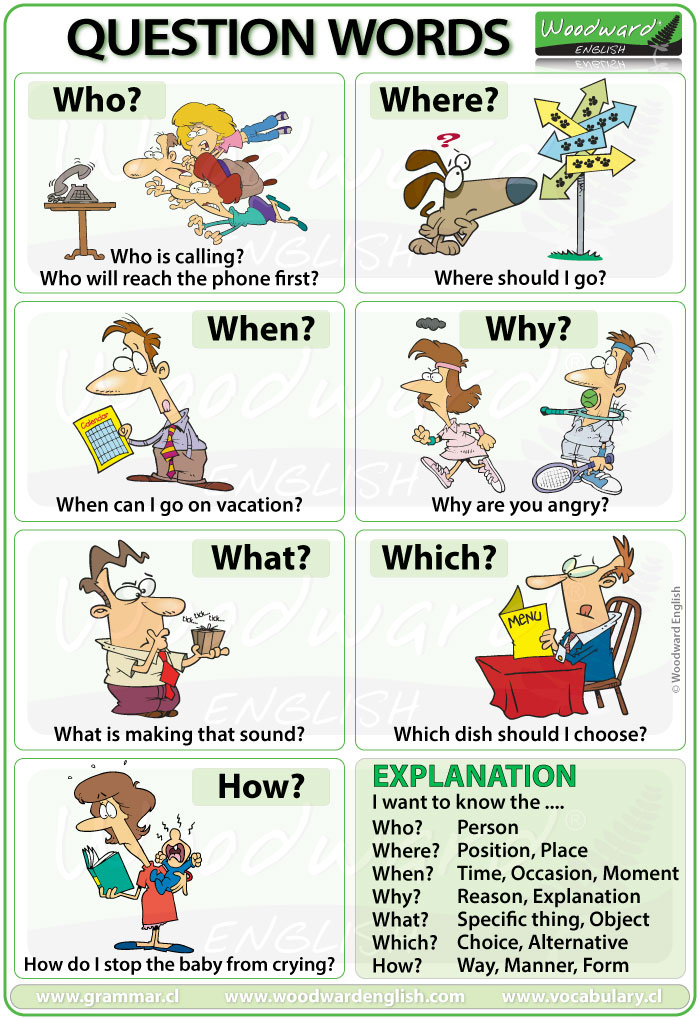
Click here, if you want to practise: https://www.grammar.cl/Games/Question_Words.htm
https://www.grammar.cl/Games/Question_Words_2.htm
REMEMBER: "TO SUCCEED,YOUR DESIRE FOR SUCCESS MUST BE GREATER THAN YOUR FEAR OF FAILURE"(Bill Cosby).